Kettlebell Workout Routines
Kettlebell Workout Routines and training has emerged as one of the most effective and versatile methods for building strength, improving cardiovascular fitness, and achieving overall body transformation.
This ancient Russian training tool has gained immense popularity in modern fitness circles due to its unique ability to combine strength training with cardiovascular conditioning in one compact workout.
Understanding Kettlebell Training
A kettlebell’s unique design, with its offset center of mass, creates an unstable force that requires additional stabilization during exercises.
his design makes it particularly effective for developing functional strength and core stability. Unlike traditional dumbbells, kettlebells engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to more efficient workouts and better results.
Key Benefits of Kettlebell Training
Strength Development The dynamic nature of kettlebell exercises promotes full-body strength development through compound movements. These movements engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater overall strength gains.
Cardiovascular Conditioning Kettlebell workouts elevate heart rate quickly and maintain it throughout the session, providing excellent cardiovascular benefits while building strength.
Core Stability and Power The offset weight of kettlebells naturally engages your core muscles during every exercise, helping develop rock-solid stability and rotational power.
Essential Kettlebell Exercises
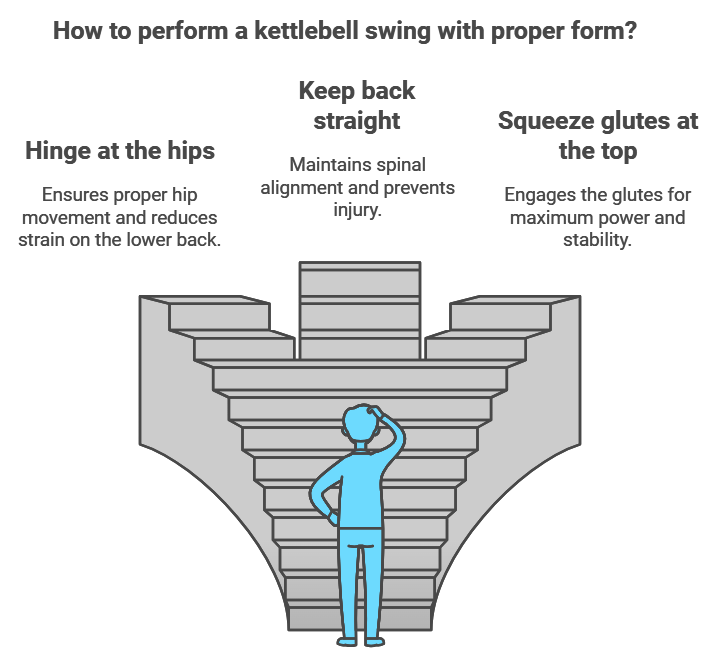
The Kettlebell Swing The foundation of kettlebell training, this explosive movement targets:
- Posterior chain muscles
- Core stability
- Hip power
- Cardiovascular endurance
The Goblet Squat A fundamental movement that builds lower body strength while maintaining proper form:
- Quadriceps engagement
- Core stability
- Upper back strength
- Proper squat pattern development
Programming Your Workout
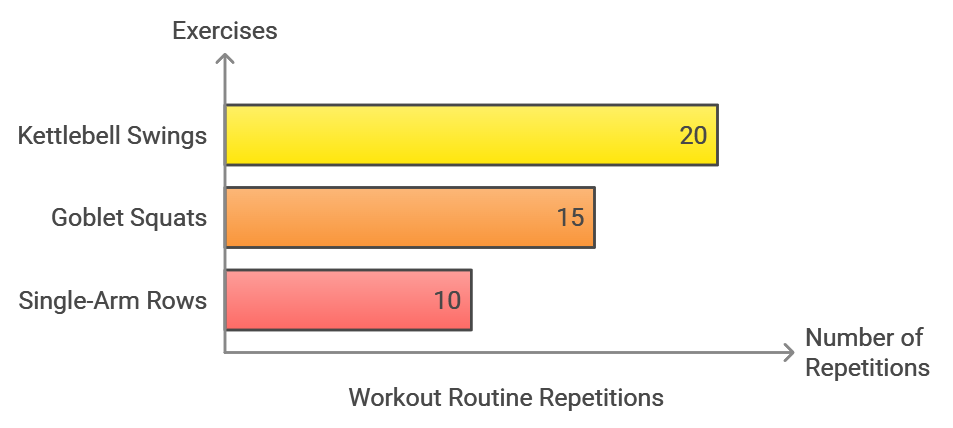
Beginner Routine
- Kettlebell swings: 3 sets of 10 reps
- Goblet squats: 3 sets of 8 reps
- Single-arm rows: 2 sets of 8 reps per side
- Rest periods: 60-90 seconds between sets
Intermediate Circuit
Form and Safety Guidelines
Proper Grip Technique The kettlebell grip is crucial for safety and effectiveness:
- Hook grip for swings
- Rack position for cleans
- Bottoms-up grip for advanced movements
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using momentum instead of muscle
- Rounding the back during swings
- Improper breathing patterns
- Choosing too heavy weights initially
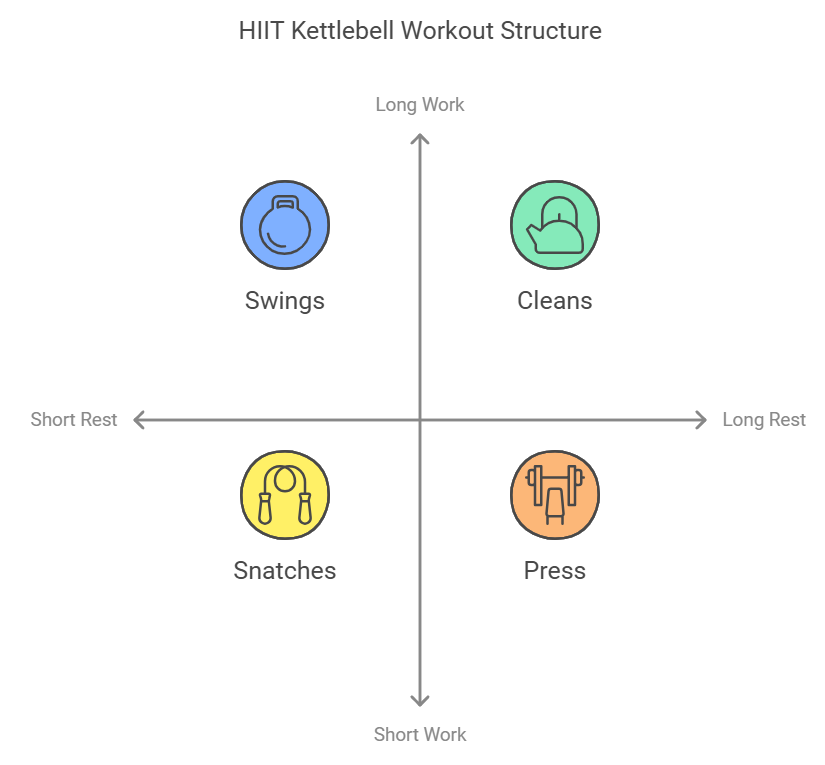
Advanced Programming
Frequently Asked Questions
What weight should beginners start with? Most men should start with 16kg (35lbs), while women typically begin with 8kg (18lbs). Focus on form before increasing weight.
How often should I train with kettlebells? Begin with 2-3 sessions per week, allowing for adequate recovery between workouts. As you progress, you can increase frequency based on your goals and recovery capacity.
Can kettlebells replace traditional weight training? While kettlebells provide excellent full-body workouts, they work best as part of a comprehensive training program that includes various training modalities.
Foundations and Essential Knowledge
The resurgence of kettlebell training marks one of the most significant shifts in modern fitness culture.
These cast-iron weights, shaped like cannonballs with handles, originated in 18th century Russia as tools for weighing crops.
Today, they’ve become indispensable in gyms worldwide, offering a unique blend of strength, cardiovascular, and mobility training in one compact tool.
The Science Behind Kettlebell Training
Recent research from the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research demonstrates that Kettlebell Workout Routines can significantly improve both maximal and explosive strength.
The offset center of mass creates an unstable load, engaging more muscle fibers than traditional weights.
This instability triggers greater neuromuscular adaptation, leading to improved functional strength and movement patterns.
Biomechanical Advantages The unique design of kettlebells allows for fluid, ballistic movements that aren’t possible with conventional weights. The handle position creates a longer lever arm, increasing the work required by stabilizing muscles and intensifying the training effect on your core musculature.
Comprehensive Benefits
Strength Development
- Increases in both maximal and explosive strength
- Enhanced grip strength and forearm development
- Improved posterior chain activation
- Superior core engagement through offset loading
Cardiovascular Enhancement Studies show that high-intensity kettlebell workouts can burn up to 20 calories per minute, rivaling the caloric expenditure of running at a 6-minute mile pace. The combination of strength and cardio makes kettlebell training particularly efficient for:
- Improved heart rate variability
- Enhanced VO2 max
- Better endurance capacity
- Increased metabolic rate
Mobility and Flexibility Dynamic kettlebell movements improve:
- Hip mobility through deep hip hinging
- Shoulder range of motion
- Thoracic spine mobility
- Ankle flexibility
Essential Kettlebell Exercises
The Fundamental Six
- Kettlebell Swing
- Primary muscles: Glutes, hamstrings, core
- Secondary muscles: Lats, shoulders, forearms
- Technical points:
- Hip hinge is primary movement
- Neutral spine throughout
- Power from hip snap
- Arms as rope, not muscle
- Turkish Get-Up
- Full-body integration exercise
- Develops shoulder stability
- Improves core strength
- Enhances body awareness
- Progressive movement patterns:
- Roll to elbow
- Sweep leg through
- Lunge position
- Standing completion
- Goblet Squat
- Anterior core loading
- Natural movement pattern
- Key teaching points:
- Elbows track inside knees
- Maintain upright torso
- Full depth achievement
- Proper knee tracking
- Single-Arm Row
- Unilateral back development
- Core anti-rotation
- Technical aspects:
- Stable hip hinge
- Packed shoulder
- Controlled eccentric
- Full range of motion
- Clean and Press
- Power development
- Shoulder stability
- Technical sequence:
- Clean to rack position
- Proper press mechanics
- Controlled descent
- Fluid movement pattern
- Racked Carry
- Loaded locomotion
- Core stability
- Shoulder endurance
- Grip strength development
Form and Technique Mastery
Breathing Patterns
- Inhale during tension release
- Exhale during force production
- Maintain braced core
- Sync breath with movement
Grip Variations
- Standard grip
- Bottom-up grip
- Hook grip
- Mixed grip
Programming and Application
Kettlebell Workout Routines
Beginner’s Foundation Program Monday/Wednesday/Friday
Warm-up:
- Halos: 5 each direction
- Hip bridges: 10 reps
- Bird dogs: 5 each side
Main workout:
1. Two-handed swings: 5x10
2. Goblet squats: 3x8
3. Single-arm rows: 3x8 each
4. Farmers walks: 3x30 seconds
Intermediate Power Building
Circuit (4 rounds):
1. One-arm swings: 12 each
2. Clean and press: 8 each
3. Racked squats: 10 each
4. Turkish get-ups: 2 each
Rest: 90 seconds between rounds
Advanced Performance Protocol
EMOM for 20 minutes:
Minute 1: 20 swings
Minute 2: 10 clean and press (5 each)
Minute 3: 15 goblet squats
Minute 4: 10 racked reverse lunges
Minute 5: Max Turkish get-ups
Programming Variables
Volume Progression Week 1-2: Focus on form
- Low volume
- Perfect technique
- Build movement patterns
Week 3-4: Increase workload
- Add sets
- Increase reps
- Maintain form quality
Week 5-6: Performance phase
- Complex movements
- Higher intensity
- Reduced rest periods
Recovery and Nutrition
Post-workout Recovery
- Active recovery methods
- Mobility work
- Proper cool-down
- Nutrition timing
Nutrition Guidelines
- Pre-workout nutrition
- Post-workout refueling
- Daily protein requirements
- Hydration protocols
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What weight should I start with? Men typically start with 16kg (35lbs), women with 8kg (18lbs). Focus on mastering form before progressing to heavier weights.
Q: How often should I train with kettlebells? Begin with 3 sessions per week, allowing 48 hours between workouts. Advanced users can train 4-5 times weekly with proper programming.
Q: Can I build muscle with kettlebells alone? Yes, kettlebell training can build significant muscle mass through progressive overload and proper programming. Focus on compound movements and adequate recovery.
Q: How long should a kettlebell workout last? Effective workouts typically range from 20-45 minutes, depending on intensity and goals. Quality movements matter more than duration.
Progress Tracking
Performance Metrics
- Track total volume
- Monitor rest periods
- Record weight progression
- Note technical improvements
Assessment Tools
- Video analysis
- Strength benchmarks
- Mobility screening
- Recovery quality
Conclusion
Kettlebell training represents a perfect blend of strength, conditioning, and mobility work.
By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll develop functional strength, improve cardiovascular fitness, and enhance overall movement quality.
Remember to prioritize technique, progress gradually, and listen to your body’s response to training.
With consistent practice and proper progression, kettlebell training can transform your fitness journey and help you achieve your physical goals efficiently and effectively.
It’s a versatile workout that combines strength, cardiovascular conditioning, and functional movement patterns.
By following proper progression and focusing on technique, you can achieve remarkable results with these versatile tools.
Remember to start conservatively, master the basics, and gradually increase complexity and intensity as you become more proficient.


